# 示例讲解PostgreSQL表分区的三种方式
# 1 简介
表分区是解决一些因单表过大引用的性能问题的方式,比如某张表过大就会造成查询变慢,可能分区是一种解决方案。一般建议当单表大小超过内存就可以考虑表分区了。PostgreSQL的表分区有三种方式:
- Range:范围分区;
- List:列表分区;
- Hash:哈希分区。
本文通过示例讲解如何进行这三种方式的分区。
# 2 例讲三种方式
为方便,我们通过Docker的方式启动一个PostgreSQL,可参考:《Docker启动PostgreSQL并推荐几款连接工具 (opens new window)》。我们要选择较高的版本,否则不支持Hash分区,命令如下:
docker run -itd \
--name pkslow-postgres \
-e POSTGRES_DB=pkslow \
-e POSTGRES_USER=pkslow \
-e POSTGRES_PASSWORD=pkslow \
-p 5432:5432 \
postgres:13
# 2.1 Range范围分区
先创建一张表带有年龄,然后我们根据年龄分段来进行分区,创建表语句如下:
CREATE TABLE pkslow_person_r (
age int not null,
city varchar not null
) PARTITION BY RANGE (age);
这个语句已经指定了按age字段来分区了,接着创建分区表:
create table pkslow_person_r1 partition of pkslow_person_r for values from (MINVALUE) to (10);
create table pkslow_person_r2 partition of pkslow_person_r for values from (11) to (20);
create table pkslow_person_r3 partition of pkslow_person_r for values from (21) to (30);
create table pkslow_person_r4 partition of pkslow_person_r for values from (31) to (MAXVALUE);
这里创建了四张分区表,分别对应年龄是0到10岁、11到20岁、21到30岁、30岁以上。
接着我们插入一些数据:
insert into pkslow_person_r(age, city) VALUES (1, 'GZ');
insert into pkslow_person_r(age, city) VALUES (2, 'SZ');
insert into pkslow_person_r(age, city) VALUES (21, 'SZ');
insert into pkslow_person_r(age, city) VALUES (13, 'BJ');
insert into pkslow_person_r(age, city) VALUES (43, 'SH');
insert into pkslow_person_r(age, city) VALUES (28, 'HK');
可以看到这里的表名还是pkslow_person_r,而不是具体的分区表,说明对于客户端是无感知的。
我们查询也一样的:
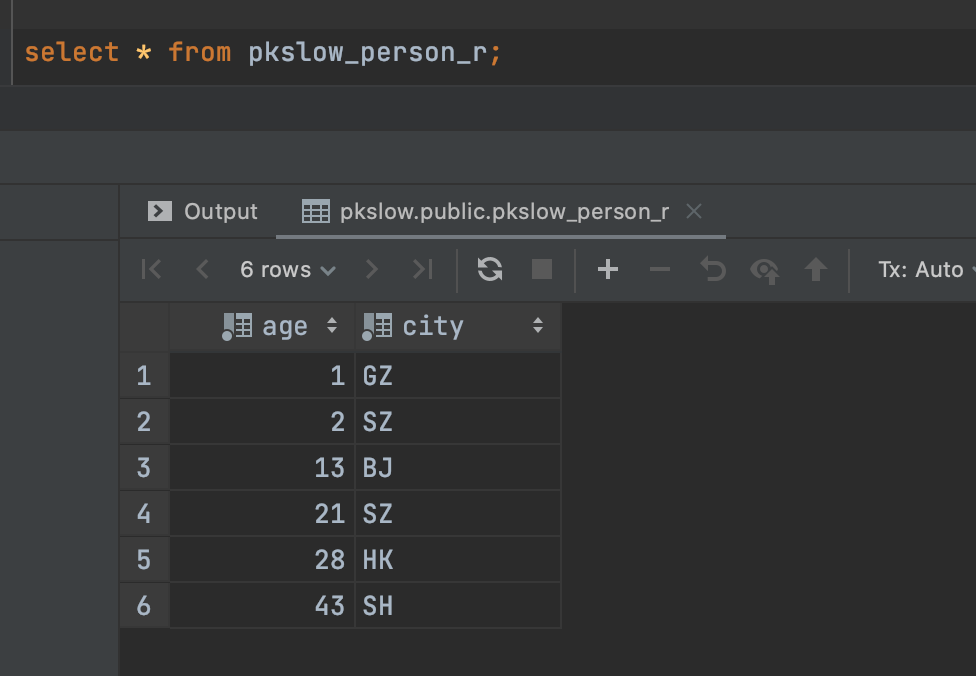
但实际上是有分区表存在的:
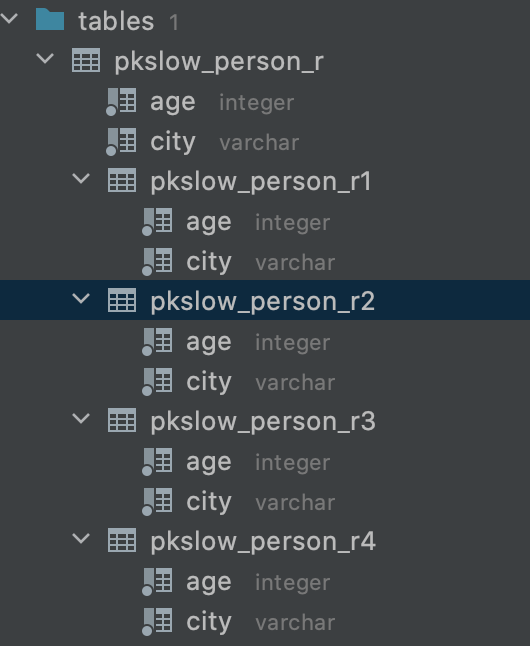
而且分区表与主表的字段是一致的。
查询分区表,就只能查到那个特定分区的数据了:
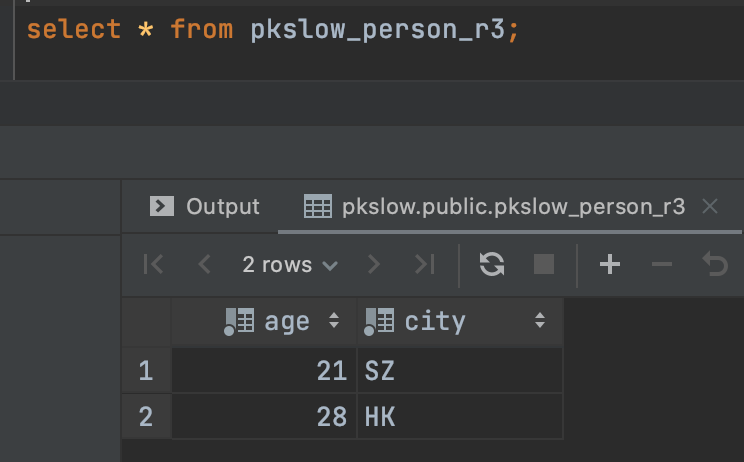
# 2.2 List列表分区
类似的,列表分区是按特定的值来分区,比较某个城市的数据放在一个分区里。这里不再给出每一步的讲解,代码如下:
-- 创建主表
create table pkslow_person_l (
age int not null,
city varchar not null
) partition by list (city);
-- 创建分区表
CREATE TABLE pkslow_person_l1 PARTITION OF pkslow_person_l FOR VALUES IN ('GZ');
CREATE TABLE pkslow_person_l2 PARTITION OF pkslow_person_l FOR VALUES IN ('BJ');
CREATE TABLE pkslow_person_l3 PARTITION OF pkslow_person_l DEFAULT;
-- 插入测试数据
insert into pkslow_person_l(age, city) VALUES (1, 'GZ');
insert into pkslow_person_l(age, city) VALUES (2, 'SZ');
insert into pkslow_person_l(age, city) VALUES (21, 'SZ');
insert into pkslow_person_l(age, city) VALUES (13, 'BJ');
insert into pkslow_person_l(age, city) VALUES (43, 'SH');
insert into pkslow_person_l(age, city) VALUES (28, 'HK');
insert into pkslow_person_l(age, city) VALUES (28, 'GZ');
当我们查询第一个分区的时候,只有广州的数据:
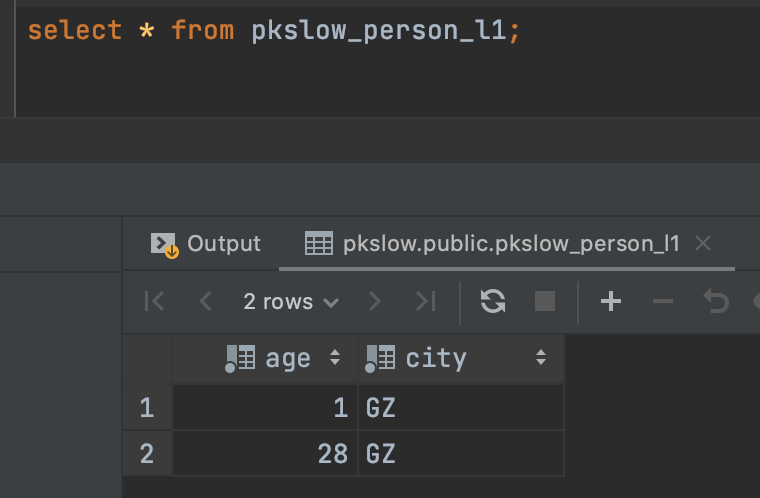
# 2.3 Hash哈希分区
哈希分区是指按字段取哈希值后再分区。具体的语句如下:
-- 创建主表
create table pkslow_person_h (
age int not null,
city varchar not null
) partition by hash (city);
-- 创建分区表
create table pkslow_person_h1 partition of pkslow_person_h for values with (modulus 4, remainder 0);
create table pkslow_person_h2 partition of pkslow_person_h for values with (modulus 4, remainder 1);
create table pkslow_person_h3 partition of pkslow_person_h for values with (modulus 4, remainder 2);
create table pkslow_person_h4 partition of pkslow_person_h for values with (modulus 4, remainder 3);
-- 插入测试数据
insert into pkslow_person_h(age, city) VALUES (1, 'GZ');
insert into pkslow_person_h(age, city) VALUES (2, 'SZ');
insert into pkslow_person_h(age, city) VALUES (21, 'SZ');
insert into pkslow_person_h(age, city) VALUES (13, 'BJ');
insert into pkslow_person_h(age, city) VALUES (43, 'SH');
insert into pkslow_person_h(age, city) VALUES (28, 'HK');
可以看到创建分区表的时候,我们用了取模的方式,所以如果要创建N个分区表,就要取N取模。
随便查询一张分区表如下:
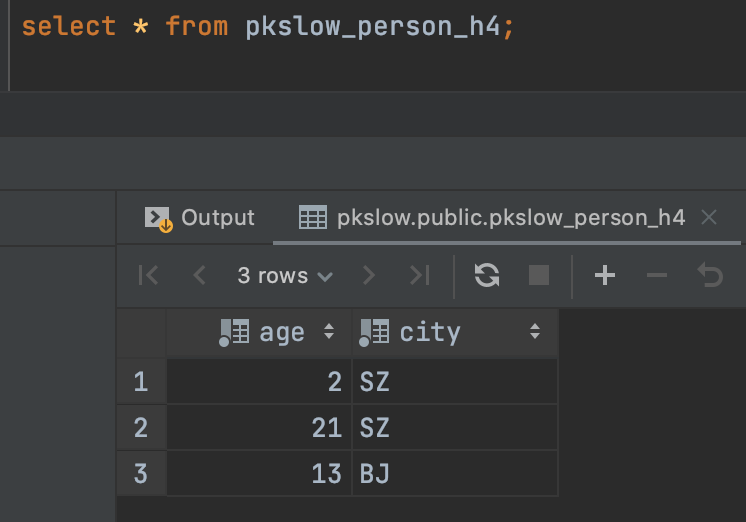
可以看到同是SZ的哈希值是一样的,肯定会分在同一个分区,而BJ的哈希值取模后也属于同一个分区。
# 3 总结
本文讲解了PostgreSQL分区的三种方式。
代码请查看:https://github.com/LarryDpk/pkslow-samples
Reference:
Postgresql Table Partitioning (opens new window)
How to use table partitioning to scale PostgreSQL (opens new window)