# Provision the Google Kubernetes Engine(GKE) with gcloud and access with kubectl
# 1 Introduction
GKE(Google Kubernetes Engine) is a k8s platform, we can use gcloud to create a GKE cluster. For GCP initiation, can go to: How to initiate the GCP project and use gcloud to access (opens new window).
# 2 Create the GKE Cluster
# 2.1 Enable API
We need to enable the API before creating the GKE:
$ gcloud services enable compute.googleapis.com
$ gcloud services enable container.googleapis.com
# 2.2 Create the Cluster
Check the machine type list and select what you want:
$ gcloud compute machine-types list | grep us-west
I select n1-standard-1 to save money. Use gcloud container clusters create to create cluster:
$ gcloud container clusters create pkslow-k8s \
--zone us-west1-a \
--cluster-version 1.20.10-gke.1600 \
--machine-type n1-standard-1
WARNING: Currently VPC-native is not the default mode during cluster creation. In the future, this will become the default mode and can be disabled using `--no-enable-ip-alias` flag. Use `--[no-]enable-ip-alias` flag to suppress this warning.
WARNING: Starting with version 1.18, clusters will have shielded GKE nodes by default.
WARNING: Your Pod address range (`--cluster-ipv4-cidr`) can accommodate at most 1008 node(s).
WARNING: Starting with version 1.19, newly created clusters and node-pools will have COS_CONTAINERD as the default node image when no image type is specified.
Creating cluster pkslow-k8s in us-west1-a...done.
Created [https://container.googleapis.com/v1/projects/pkslow/zones/us-west1-a/clusters/pkslow-k8s].
To inspect the contents of your cluster, go to: https://console.cloud.google.com/kubernetes/workload_/gcloud/us-west1-a/pkslow-k8s?project=pkslow
kubeconfig entry generated for pkslow-k8s.
NAME LOCATION MASTER_VERSION MASTER_IP MACHINE_TYPE NODE_VERSION NUM_NODES STATUS
pkslow-k8s us-west1-a 1.20.10-gke.1600 34.82.42.67 n1-standard-1 1.20.10-gke.1600 3 RUNNING
# 2.3 Check with commands
After created, check the version and nodes:
$ kubectl version
Client Version: version.Info{Major:"1", Minor:"19", GitVersion:"v1.19.3", GitCommit:"1e11e4a2108024935ecfcb2912226cedeafd99df", GitTreeState:"clean", BuildDate:"2020-10-14T12:50:19Z", GoVersion:"go1.15.2", Compiler:"gc", Platform:"darwin/amd64"}
Server Version: version.Info{Major:"1", Minor:"20+", GitVersion:"v1.20.10-gke.1600", GitCommit:"ef8e9f64449d73f9824ff5838cea80e21ec6c127", GitTreeState:"clean", BuildDate:"2021-09-06T09:24:20Z", GoVersion:"go1.15.15b5", Compiler:"gc", Platform:"linux/amd64"}
$ kubectl get node
NAME STATUS ROLES AGE VERSION
gke-pkslow-k8s-default-pool-4743a88e-175c Ready <none> 59s v1.20.10-gke.1600
gke-pkslow-k8s-default-pool-4743a88e-71l6 Ready <none> 58s v1.20.10-gke.1600
gke-pkslow-k8s-default-pool-4743a88e-9wn2 Ready <none> 59s v1.20.10-gke.1600
The gcloud command will help to add context for us:
$ kubectl config get-contexts
CURRENT NAME CLUSTER AUTHINFO NAMESPACE
docker-desktop docker-desktop docker-desktop
* gke_pkslow_us-west1-a_pkslow-k8s gke_pkslow_us-west1-a_pkslow-k8s gke_pkslow_us-west1-a_pkslow-k8s
If you have no right, try with below:
$ gcloud container clusters get-credentials pkslow-k8s --zone=us-west1-a
Check the Pods:
$ kubectl get pod -A
NAMESPACE NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE
kube-system event-exporter-gke-67986489c8-2lvtj 2/2 Running 0 4m14s
kube-system fluentbit-gke-6xdgs 2/2 Running 0 3m59s
kube-system fluentbit-gke-92swm 2/2 Running 0 3m58s
kube-system fluentbit-gke-xrj9q 2/2 Running 0 3m59s
kube-system gke-metrics-agent-9z2m2 1/1 Running 0 3m59s
kube-system gke-metrics-agent-f5kj2 1/1 Running 0 3m59s
kube-system gke-metrics-agent-jwsnk 1/1 Running 0 3m58s
kube-system konnectivity-agent-686dbcf84c-852jd 1/1 Running 0 3m28s
kube-system konnectivity-agent-686dbcf84c-sx8rk 1/1 Running 0 4m9s
kube-system konnectivity-agent-686dbcf84c-vz68j 1/1 Running 0 3m29s
kube-system konnectivity-agent-autoscaler-6cb774c9cc-j6s2t 1/1 Running 0 4m9s
kube-system kube-dns-autoscaler-844c9d9448-t545t 1/1 Running 0 4m9s
kube-system kube-dns-b4f5c58c7-psxrv 4/4 Running 0 4m10s
kube-system kube-dns-b4f5c58c7-v7phb 4/4 Running 0 3m34s
kube-system kube-proxy-gke-pkslow-k8s-default-pool-4743a88e-175c 1/1 Running 0 2m34s
kube-system kube-proxy-gke-pkslow-k8s-default-pool-4743a88e-71l6 1/1 Running 0 3m53s
kube-system kube-proxy-gke-pkslow-k8s-default-pool-4743a88e-9wn2 1/1 Running 0 2m56s
kube-system l7-default-backend-56cb9644f6-5qzsr 1/1 Running 0 4m15s
kube-system metrics-server-v0.3.6-9c5bbf784-xrksq 2/2 Running 0 3m19s
kube-system pdcsi-node-7d7gp 2/2 Running 0 3m58s
kube-system pdcsi-node-cx4dp 2/2 Running 0 3m59s
kube-system pdcsi-node-zz2hv 2/2 Running 0 3m59s
# 2.4 Check on the Console
We can visit the GCP console to check all the details:
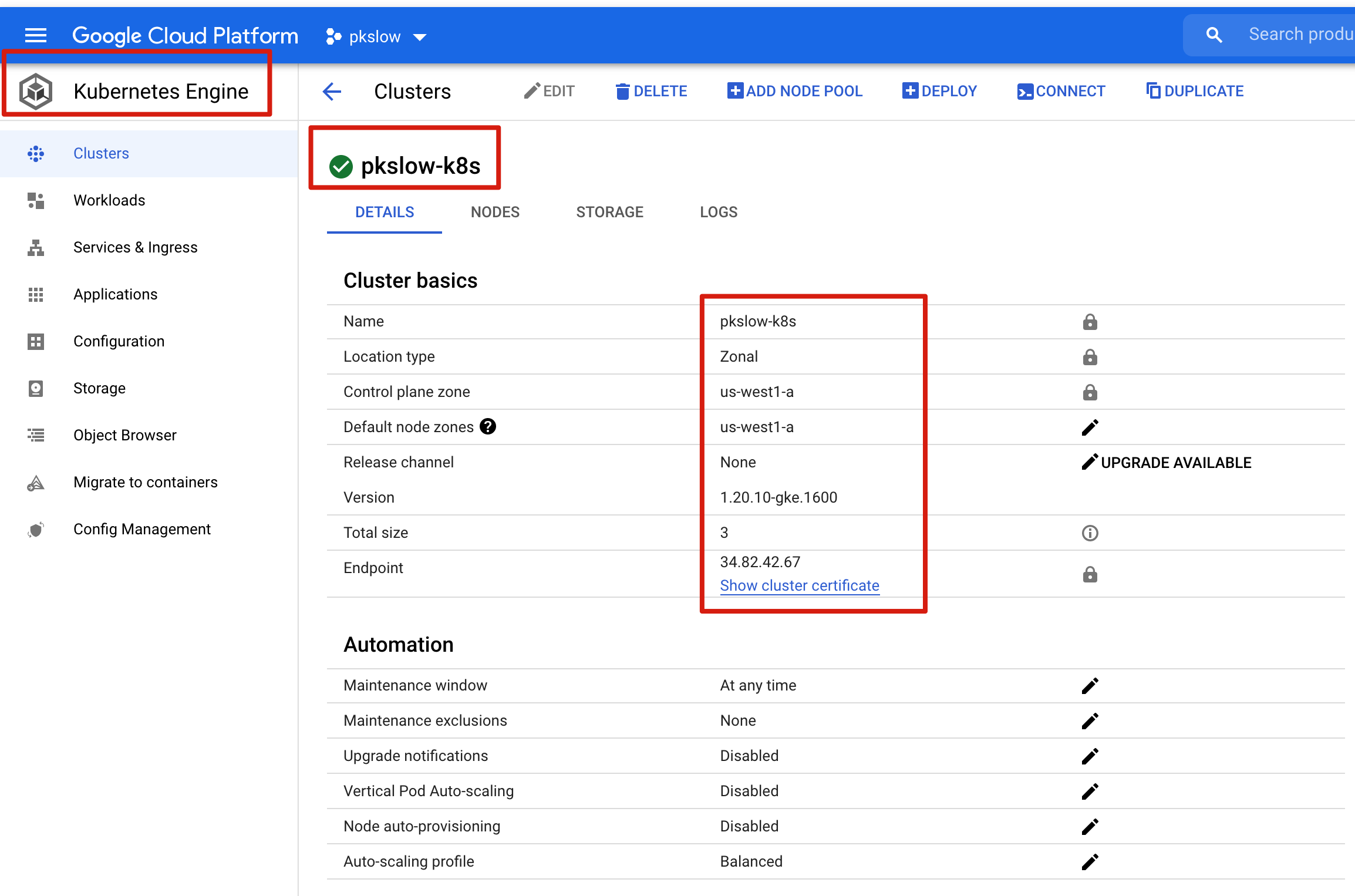
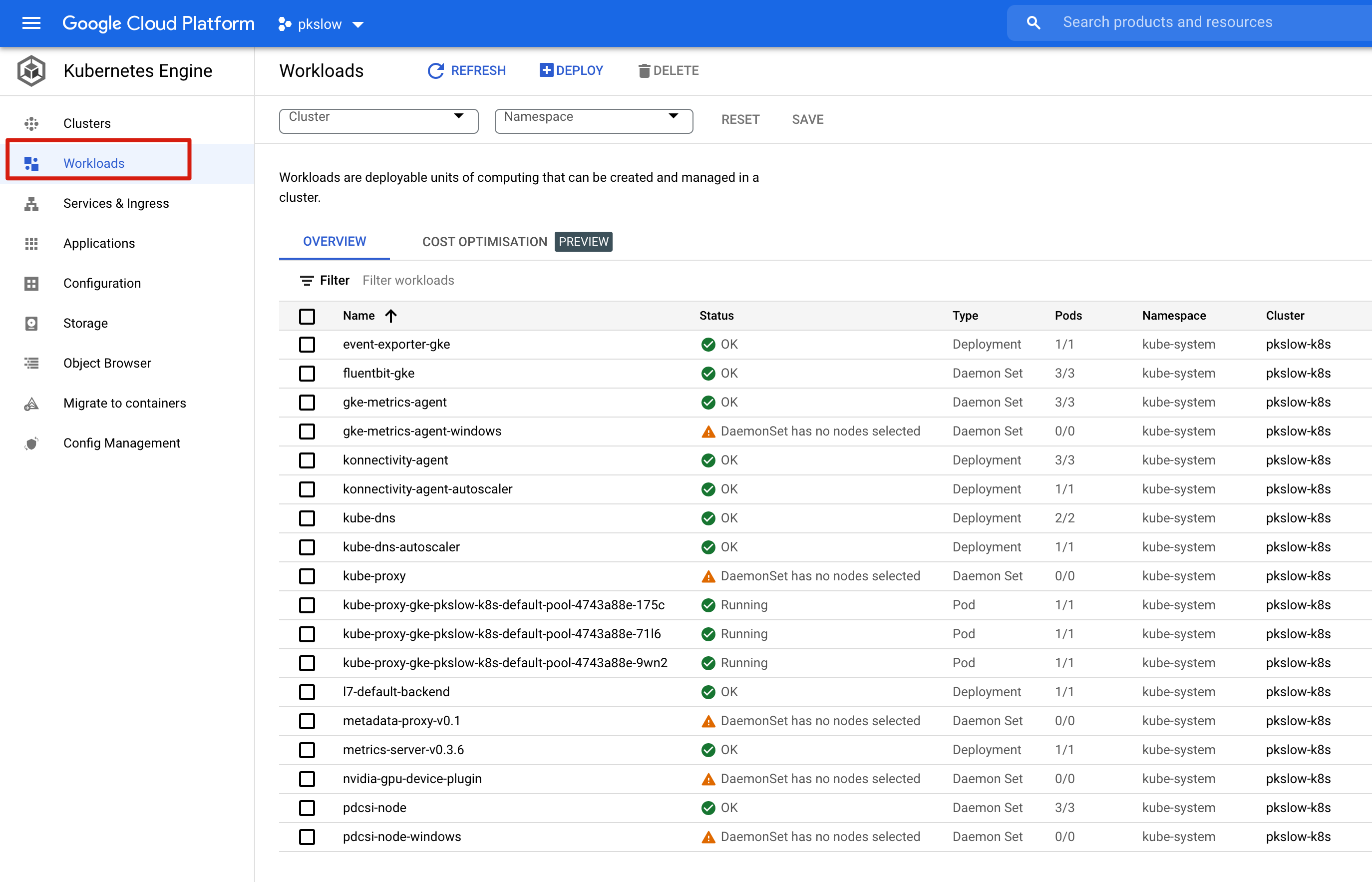
We can check the Deployment, DaemonSet on console:
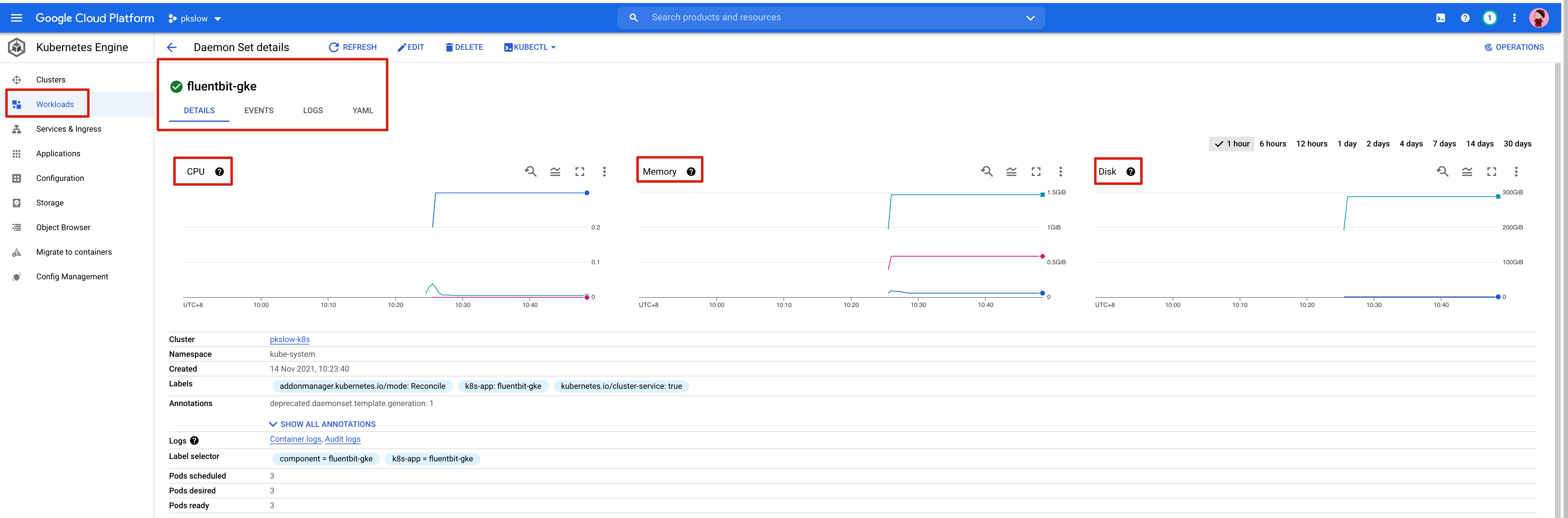
For more detail, we can check the CPU/Memory/Disk/Log:
# 3 Virtual Machines
To start the cluster, GCP would create the VMs as k8s Nodes:
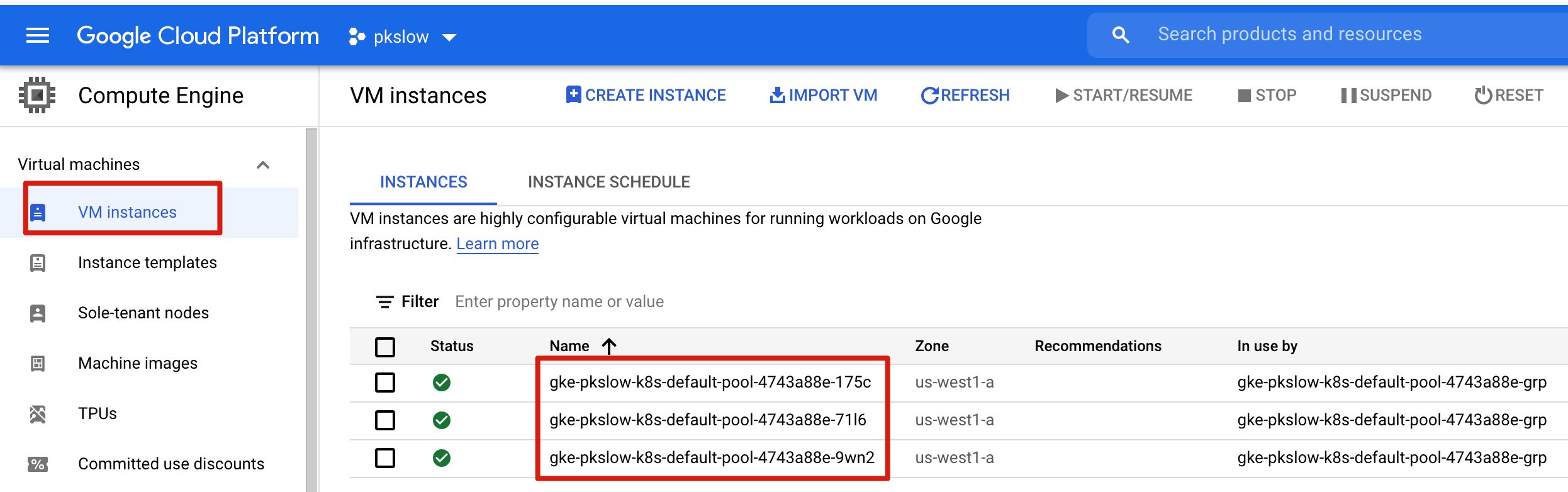
We can list the VMs with gcloud:
$ gcloud compute instances list
NAME ZONE MACHINE_TYPE PREEMPTIBLE INTERNAL_IP EXTERNAL_IP STATUS
gke-pkslow-k8s-default-pool-4743a88e-175c us-west1-a n1-standard-1 10.138.0.3 34.105.xx.xxx RUNNING
gke-pkslow-k8s-default-pool-4743a88e-71l6 us-west1-a n1-standard-1 10.138.0.2 35.247.xx.xxx RUNNING
gke-pkslow-k8s-default-pool-4743a88e-9wn2 us-west1-a n1-standard-1 10.138.0.4 35.199.xx.xxx RUNNING
For troubleshooting, we can ssh to the VM:
$ gcloud compute ssh gke-pkslow-k8s-default-pool-4743a88e-175c --zone=us-west1-a

For logging, we can see all the log on console:

# 4 Delete the cluster
After we completed the lab, we can delete the cluster:
$ gcloud container clusters delete pkslow-k8s --zone us-west1-a
Reference:
gcloud container (opens new window)
Provisioning Kubernetes clusters on GCP with Terraform and GKE (opens new window)